To care for a patient living with diabetes will require a multifaceted and compassionate approach. Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and its management is crucial for preventing complications and improving the patient’s overall quality of life. As a healthcare provider or caregiver, your role in supporting individuals with diabetes is of utmost importance in empowering them to effectively manage their condition.
Here we discuss essential ways to provide quality care for a patient living with diabetes, offering in-depth strategies and detailed tips to ensure their well-being and confidence in diabetes self-management. Understanding and implementing these approaches can make a significant difference in your patient’s health outcomes, helping them lead a fulfilling life while successfully navigating the challenges posed by diabetes.
Keep in mind that some of these insights may require lifestyle changes, medication, and assistance in setting realistic and achievable health goals. On the other hand, keep in mind that every patient’s experience with diabetes is unique and personalized care plays a pivotal role in achieving positive outcomes.
This will help you care for a patient living with diabetes toward better self-management, enhanced quality of life, and reduced risk of complications and will help you become an invaluable ally in your patient’s diabetes journey, supporting them in their efforts to lead healthy, fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this chronic condition.
15 Ways To Care For A Patient Living With Diabetes
These strategies may not come as a piece of medical advice, but from our years of offering care to people living with diabetes, we have seen these steps to be effective to care for them. So, here are some ways to care for a patient living with diabetes:
#1. Educate Yourself About Diabetes
WHO describes diabetes as a chronic, metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose (or blood sugar), which leads over time to serious damage to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Before caring for a patient living with diabetes, you have to understand this ailment and its signs and symptoms.
Understand diabetes, including the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Know the role of insulin and how the body processes glucose. Use visual aids, pamphlets, and educational videos to enhance understanding. Cover topics like blood sugar testing, symptoms of high and low blood sugar, and the importance of timely medical attention.
#2. Encourage Patient To Go On Regular Medical Checkups
Set up a schedule for regular checkups and follow-ups with a diabetes specialist or primary care physician. During these visits, review the patient’s blood glucose logs, check for any concerning trends, and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Screen for complications like retinopathy, nephropathy, and cardiovascular disease.
#3. Personalized Meal Planning
Work closely with a registered dietitian to create a meal plan that aligns with the patient’s cultural preferences and lifestyle.
Emphasize portion control and nutrient-dense foods while limiting sugary and processed items. Teach them how to read food labels and estimate carbohydrate counts.
#4. Promote Physical Activity
Collaborate with a physical therapist or exercise specialist to design an exercise regimen that suits the patient’s physical abilities and medical conditions.
Encourage a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Provide guidance on safely managing blood sugar levels during physical activity. See some fitness suggestions you can adopt.
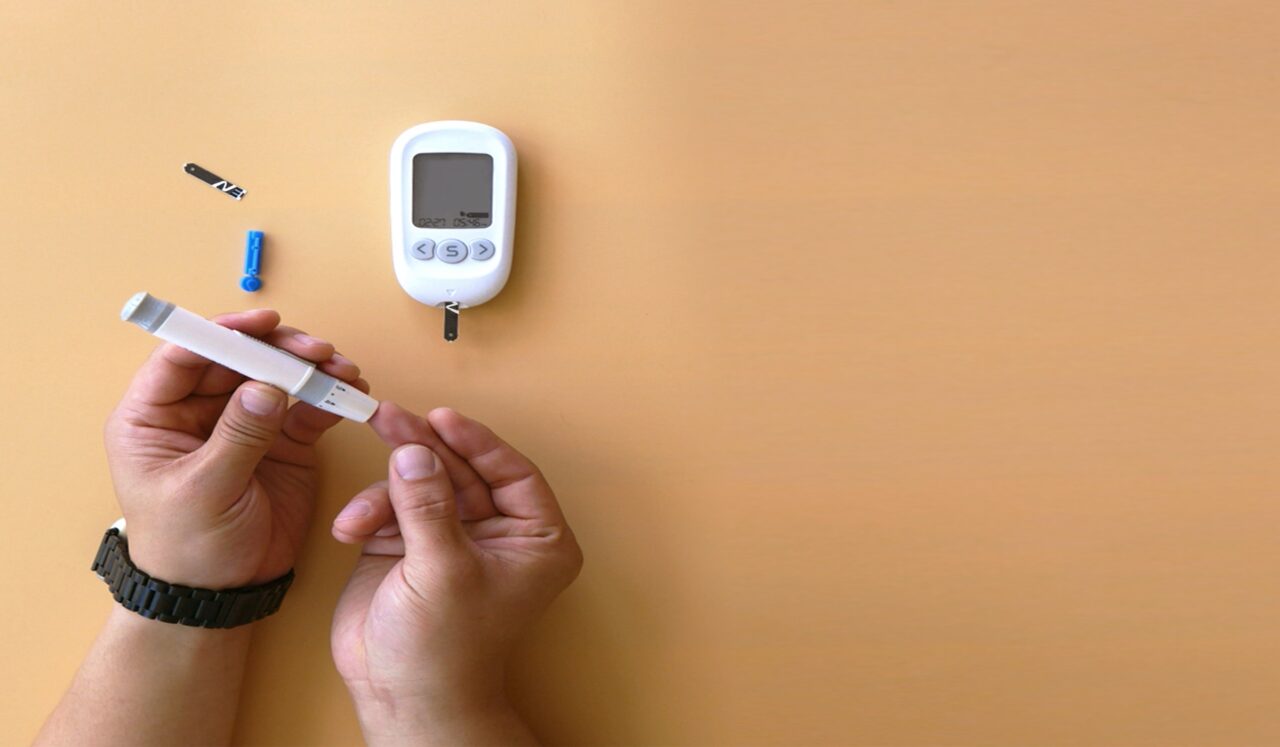
#5. Monitor Blood Glucose Levels
Know how to use a blood glucose meter correctly and review the target blood sugar range with the patient. Help them identify patterns in their readings and adjust their treatment plan accordingly.
Discuss factors that can influence blood sugar levels, such as illness, stress, and changes in physical activity, and help them keep their sugar level at an optimal level.
#6. Manage The Patients Medication
Simplify the medication schedules of your patient and explain the purpose of each drug the patient is taking. Discuss potential side effects and how to manage them.
Use tools like pill organizers and smartphone reminders to help the patient stay on track with their medications. And when a medication is administered, do well to Dispose Of Medical Waste appropriately.
#7. Ensure The Patient Is Not Stressed
Encourage the patient to practice stress-reducing techniques like mindfulness, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery.
Also, encourage the patient to engage in activities they find relaxing, such as reading, painting, or spending time in nature. Discuss the link between stress and blood sugar fluctuations to highlight the importance of stress management.
While you are managing stress for your patient, give yourself some time out too. Utilize this Self-care For Caregivers guide to know how best.
#8. Encourage The Patient To Take On a Foot Care Routine
With diabetes comes foot sores and blisters. To effectively care for a patient living with diabetes, you must educate and enlighten them on what this is and why routine care is important.
Educate the patient on proper foot care, stressing the need for daily foot inspections and prompt treatment of any cuts, blisters, or sores. Emphasize the importance of wearing comfortable and supportive footwear to prevent foot injuries.
#9. Encourage The Patient To Join A Support Group
One way to get your patient out of their head is to have them be in a support group. Encourage the patient to attend diabetes support groups, either in person or online.
Being part of a community of individuals facing similar challenges can offer valuable emotional support and practical tips for diabetes management. Engage family members and close friends to provide a strong support network.
#10. Keep In Step With Diabetes Technology
Stay informed about the latest diabetes technologies, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and insulin pumps.
Discuss with the patient if these tools align with their lifestyle and health goals, and provide assistance in using and interpreting the data they generate.
#11. Encourage Them To Sleep Well
Highlight the importance of consistent sleep patterns and sufficient sleep duration for diabetes management. Educate the patient about the potential impact of sleep disturbances on blood sugar levels and overall health.
Encourage them to adopt healthy sleep habits. This guide 5 Benefits of Napping that Will Help You Rest Easily will be effective in convincing them.
#12. Encourage Regular Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Checks
Explain the connection between diabetes and cardiovascular health, and the increased risk of heart disease.
Encourage the patient to have regular blood pressure and cholesterol checks, and collaborate with their healthcare team to manage these risk factors through lifestyle changes and medications if necessary.
#13. Recognize Warning Signs
Provide a list of common symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
Teach the patient how to respond to these situations, including the use of glucose tablets or gel for low blood sugar and seeking medical attention for persistent high blood sugar levels.
#14. Know Diabetes-Related Complications
Explain the potential long-term complications of diabetes, such as kidney disease, eye problems, and nerve damage. Emphasize the importance of regular checkups to catch these issues early. Work with the patient to set goals for managing diabetes effectively and preventing complications.
#15. Ensure They Are Emotionally Cared For
Create a safe and non-judgmental environment for the patient to discuss their feelings and concerns related to diabetes.
Offer emotional support and empathy, and consider involving a mental health professional if the patient is struggling to cope with the emotional aspects of managing diabetes.
Conclusion
By providing detailed and personalized care, you can empower patients living with diabetes to effectively manage their condition and lead healthier lives. Stay engaged with the patient and their support system, and continuously educate yourself about diabetes advancements to deliver the best possible care.
Remember that each patient is unique, so adapting your approach to their individual needs and preferences is key to successful diabetes management.
We hope you found this guide helpful.
If you are in Indiana and looking for how to access quality care services and personalized client care plans, visit Good Hands home care agency, where care is offered with professionalism and efficiency.